You’ve probably seen a lot of presentations where the presenter points a red pointer at a wall or overhead projection that is far away. Have you ever wondered how a laser works?
Laser pointers are not as complicated as you may think. They have been around for many decades. The basis of the laser pointer is a scientific principle known as stimulated emission. Understanding how this works will help you to understand the inner workings and features of a laser.
This article will explain how does a laser pointer works and the basic technology behind lasers. This guide will help you understand lasers and impress your friends with your next presentation. Let’s get started!
Table of contents
What Is a Laser?
You may have already experienced the amazing capabilities of laser technology if you’ve seen a laser in action. What is a laser?
It’s an instrument that emits focused light beams at specific wavelengths and frequencies. It consists of three components: an amplification material, such as crystals or gases; an external energy source; and an optic cavity, which is two mirrors reflecting the light back and forth through the medium to form the beam.
Laser emitters are available in many different forms, from simple laser pointers for presentations to complex medical instruments for surgery. Each type of laser emits light in a different colour or intensity depending on the wavelength. This can vary from below visible to well beyond the visible spectrum.
We can create a wide range of tools by harnessing the technology that produces powerful but faint beams of light. With precise control over frequency, wavelength and power output, we can create amazing tools.
How do Lasers Produce Light?
The laser pointer was a light-based tool that first appeared in 1960. Its original purpose, however, was quite different from how we use it today. How does a laser work? Take a look.
A laser pointer is made up of three components at its core: an energy supply, an optical amplifier and an optical cavity. The optical amplifier amplifies the energy that is supplied by the energy source. The optical cavity then reflects the light that has been amplified back on itself, allowing it to be intensified further.
This ‘coherent’ light is then focused to create a large beam of visible light, which we can use to highlight a certain object in a presentation or make patterns on walls. Lasers are powerful beams of light that work by amplifying, focusing and concentrating light. They require special safety measures in order to avoid misuse.
What are The Parts of a Laser Pointer?
If you want to understand how laser pointers work, you should first have an idea about various essential parts of a laser pointer. Each part plays an important role in order to produce a laser beam that you can use to point at things.
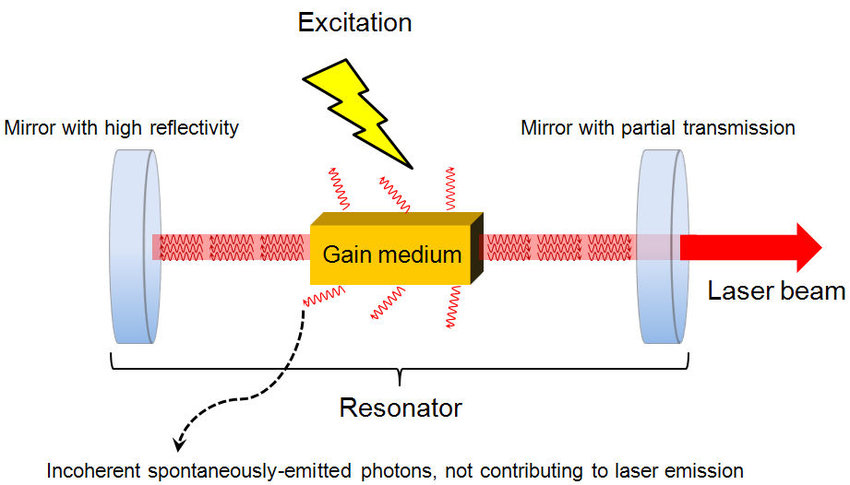
Laser Source
Laser sources are responsible for producing the beam. The laser cavity consists of three components:
- A gain medium: The gain medium (such as neodymium-doped yttrium aluminium garnet or Nd-YAG), amplifies light from the active element.
- A pumping source: An electrical current excites electrons in the gain medium and releases energy as photons.
- Mirrors: Mirrors reflect the photons, which helps to create a beam with very precise characteristics.
Optics Assembly
This part shapes, steers and focuses the laser beam to ensure it is directed precisely toward its target. Optics assemblies usually consist of two lenses – one collimating, which ensures that photons are all travelling in parallel directions and the other, which focuses on a particular point at your target location. A motorized base is also included depending on the level of sophistication of your laser pointer. This will enable you to adjust its angle much more easily.
These parts must work together perfectly to produce the laser dot you need to give a presentation of professional quality or a scientific lecture. It pays off knowing what goes into a laser pointer.
How is the Laser Beam Formed?
How does a laser beam form? The process begins with energy being pumped into the active material, also known as the optical gain media. The energy source can be electrical or chemical.
Two things happen when energy is introduced into the active material:
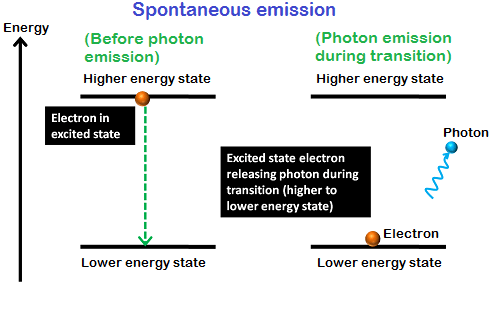
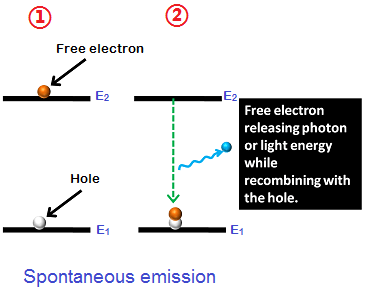
- The Stimulation Process: This is when the crystal material within a laser pointer absorbs some of the energy from the pump source and gets excited–atoms in this material jump from a low-energy state to a higher-energy state. This process is repeated until there are more atoms in the higher-energy state than in the lower-energy one.
- The Amplification Process: The excited atoms then start emitting their own photons—light particles that travel at the speed of light (literally) and get amplified due to interactions between them and other elements in their environment, like mirrors that redirect the beam back onto itself. This is what forms the real laser beam that we see with our eyes!
The Different Types of Lasers
Ever wondered how laser pointers work? There are several types of lasers and they all work differently. Here’s an overview of the main three types of lasers used in laser pointers.
Gas Lasers
Gas lasers are the first type. This type of laser produces light amplification by arousing an atom, or a group of atoms, in a medium of gas. The atom or group of atoms releases energy as visible light or infrared rays.
Diode Lasers
The second type of laser is a diode laser. This type of laser uses semiconductor materials and electrical current to create light. A diode laser has two electrodes and a chamber filled with gas–when voltage is applied, electrons move through the chamber and create light when they interact with the gas medium.
Solid-State Lasers
The third type of laser is called a solid-state laser. This type uses crystals or glasses as its lasing medium instead of gasses or liquids like other types do. The material used to create solid-state lasers has different properties than other lasing media—it provides greater stability, which makes it perfect for laser pointers.
Different Colors a Laser Can Produce
Did you know a laser can emit a variety colours? The pointer can emit a variety of colours depending on the material used. These include red, green and blue.
So how does a laser pointer create these different colours?
Laser Diode
A laser diode is at the core of a pointer laser. It is a semiconductor device with two terminals that emits laser beams when electricity is passed through it. The type of diode material determines the wavelength of the light, and therefore it’s colour.
Different Wavelengths
Different lasers emit different wavelengths. For example, red lasers emit light at a wavelength of around 650 nanometers. Blue lasers are closer to 473 nm. Green laser pointers are 532 nanometers (nm) and yellow lasers are 604 nm. Scientists have developed white lasers that emit 450-470nm wavelengths in recent years.
Power Output and Color Brightness
While some laser pointers can produce different colours, their brightness may be less than other pointers that only emit one colour. This is because the power output can differ depending on colour. For example, green lasers produce more power than red lasers. If you want something bright, eye-catching and impressive for your next lecture or presentation, opt for a colour that is all in one.
How To Boost the Power and Distance of a Laser?
You’ve come to the right place if you want to know how you can make your laser more powerful and extend its range. Here are some tips to help you make the most of your laser pointer:
Replace Batteries
To increase the distance and output of your laser, you should use high-quality, new batteries. Old or faulty batteries will drain your device’s power, so it may be time to replace them if your device isn’t delivering enough power.
Increase Beam Diameter
The beam’s diameter will determine how far it travels. If you want to get more distance, try widening the beam. You can do this by either widening the internal components of your beam or adding external optics, such as lenses or reflective mirrors, that change its trajectory and spread its light.
Use More Powerful Laser Outputs
Laser pointers are rated by their output wavelength and source of power. If you want to increase the capabilities of your device, it is important to use high-powered lasers. The higher-powered lasers will have more power, which means they’ll be able to reach further and with greater intensity. They are ideal for applications like cutting and engraving as well as visual presentations that require greater visibility.
At What Distance Can a Laser Burn?
Laser pointers are rated by their output wavelength and source of power. If you want to increase the capabilities of your device, it is important to use high-powered lasers. The higher-powered lasers will have more power, which means they’ll be able to reach further and with greater intensity. They are ideal for applications like cutting and engraving as well as visual presentations that require greater visibility.
What distance is a laser capable of burning? It is one of the more frequently asked questions about laser technology.
It really does depend on the power of your laser pointer. The more powerful the laser pointer, the greater the danger to your eyes. The majority of commercial laser pointers have a Class 2 rating, meaning that they should not cause eye damage when you stare at them directly from a distance of 1-2 feet. However, stronger lasers are dangerous even up to 30 feet.
You should not look directly into the beam of light from a handheld laser device or a laser pointed directly at another person’s eye. To be safe, use common sense to keep your laser away from people and animals.
Common Uses of Laser Pointers
It may surprise you to find out that laser pointers have many practical and useful uses. Laser pointers can be used for many purposes. They are not just a way to point fun at things.
Astronomy
Astronomy is the most common application of laser pointers. Astronomers paint stars and planets on the night sky to make them easier to track and locate. Laser pointers are also useful for measuring the angular distances of stars and planets as well as measuring distances in the solar system.
Presentations
Also, laser pointers are used in presentations at school or work. It is much more convenient to point out specific details on diagrams or slides without having directly touch them than it is to use a remote control or anything else. Laser pointers also provide an extra level of engagement for the audience by allowing them to interact with something tangible.
Education & Toys
Laser pointers can also be used for science experiments and in educational toys, such as virtual reality headsets or motion gaming consoles. These gadgets let you move about your environment while the laser beam tracks you, helping you to stay within the boundaries of your game or experience.
Conclusion
Laser pointers work very simply and are an excellent example of laser technology. Laser pointers emit a narrow light beam when the light is focused on a single spot. This is why they appear so bright. The beam can also travel a long distance before losing its intensity.
Laser technology is incredibly popular, and laser pointers can be used in a wide variety of ways. Laser pointers can be used for a variety of purposes, from public presentations to entertaining activities.



